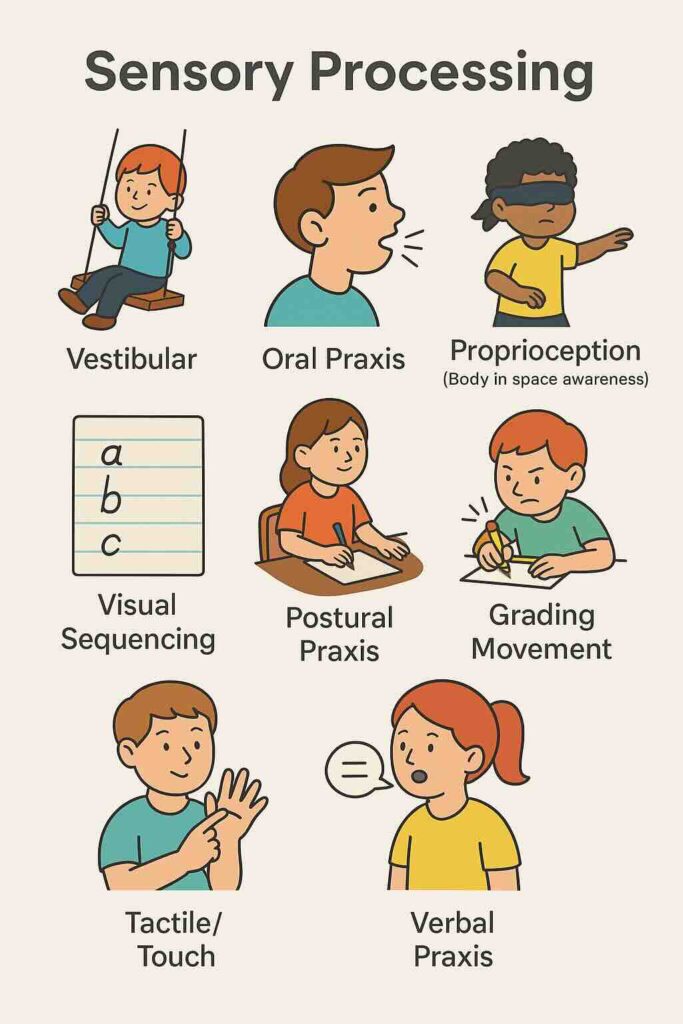
Sensory Processing
Sensory processing is how the brain takes in and makes sense of information from the body and environment. Children use this information to move, focus, write, speak, and interact with the world.
When sensory systems don’t work well together, kids may seem clumsy, overly sensitive, distracted, or disorganized—and everyday tasks like sitting still, writing, or following directions become difficult.
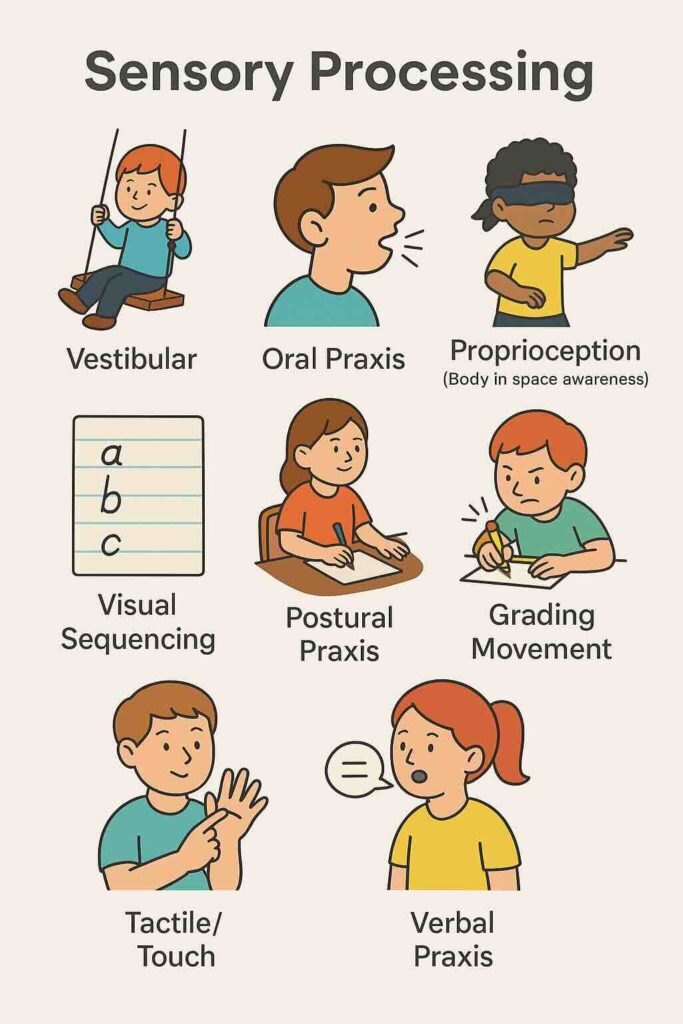
Vestibular (Balance & Movement Awareness)
- What it means: The sense of movement and balance, based in the inner ear.
- How it affects function: Helps with sitting upright, moving safely, and staying calm during motion.
- In writing: A child with poor vestibular processing may slouch, get dizzy easily, or constantly fidget during writing tasks.
Oral Praxis
- What it means: Coordinating mouth movements for speech, eating, or sound production.
- How it affects function: Supports clear speech and oral motor control.
- In learning: A child may have difficulty forming words, leading to unclear communication or hesitation when responding verbally. Tongue movement can also indicate a child’s ability to cross midline and laterality or motor coordination.
Proprioception (Body Awareness / “Where am I?†Sense)
- What it means: Knowing where your body parts are without looking.
- How it affects function: Helps with using the right amount of pressure and control.
- In writing: Kids may press too hard or too lightly with pencils, bump into desks, or shift awkwardly in their seats.
Visual Sequencing
- What it means: Following things in the correct order using vision.
- How it affects function: Needed for reading, copying, and completing steps in order.
- In writing: Kids might reverse letters, skip steps in a task, or struggle with spelling and spacing.
Postural Praxis
- What it means: Planning and carrying out whole-body movements while keeping posture.
- How it affects function: Needed for dressing, playground skills, and classroom posture.
- In writing: Kids may have difficulty sitting upright, transitioning between activities, or coordinating sitting still while using their hands.
Grading Movement
- What it means: Adjusting how much force or speed is used during a task.
- How it affects function: Needed for playing, writing, and controlling tools.
- In writing: The child may scribble too hard, break pencils, or have poor control over letter formation.
Tactile / Touch
- What it means: The ability to feel and tolerate touch on the skin.
- How it affects function: Kids may avoid messy tasks or overreact to textures (clothes, tags, tools).
- In writing: A child might dislike pencil textures, paper, or resist certain classroom materials.
Verbal Praxis
- What it means: Planning and sequencing sounds for clear speech.
- How it affects function: Helps children explain ideas, follow verbal steps, and engage in conversations.
- In learning: A child may hesitate, mispronounce, or struggle to organize words when speaking or answering questions in class.
Would you like me to now generate this infographic in JPEG format with these exact subskills and simplified labels for clarity?